Class 12 Chemistry Important MCQ Question Answer solution with pdf. Here We Provides Class 1 to 12 all Subjects NCERT Solution with Notes, Question Answer, CBSE and HBSE Important Questions, MCQ and old Question Papers for Students.
- Also Read :- HBSE Class 12 Important Questions [Latest]
HBSE ( Haryana Board ) Solution of Class 12 Chemistry MCQ important Question And Answer solution for 2025 exams.
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 – Solutions MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Mole fraction of a solute in 2.5 molal aqueous solution is:
(A) 0.43
(B) 0.043
(C) 4.3
(D) 43
Ans – (B) 0.043
2. Correct expression for elevation in boiling point is:
(A) ΔTb = Kb.m
(B) ΔT = Kf.m
(C) π = CRT
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) ΔTb = Kb.m
3. In the following compounds which has minimum boiling point? Most Important
(A) H2Se
(B) H2Te
(C) H2O
(D) H2S
Ans – (D) H2S
4. In the given Alkyl halides which one has minimum boiling point?
(A) C2H5F
(B) C2H5I
(C) C2H5Cl
(D) C2H5Br
Ans – (A) C2H5F
5. Which has Highest Boiling point ?
(A) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(B) CH3OH
(C) CH3CH2CH2OH
(D) CH3CH2OH
Ans – (A) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
6. In the following which has Highest Boiling point ?
(A) CH3Br
(B) CH3I
(C) CH3F
(D) CH3Cl
Ans – (B) CH3I
7. Maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of a liquid solvent does not depend upon :
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Nature of solute
(D) Nature of solvent
Ans – (A) Pressure
8. Low concentration of O2 in the blood of people living at high altitude is due to:
(A) Low Temperature
(B) Low Atmospheric Pressure
(C) High Atmospheric Pressure
(D) None of the above
Ans – (B) Low Atmospheric Pressure
9. The unit of ebullioscopic constant is:
(A) K kg mol–1
(B) mol kg K–1
(C) K mol kg–1
(D) None of the above
Ans – (A) K kg mol–1
10. Molarity of 900 gm of water is:
(A) 50 M
(B) 55.5 M
(C) 5 M
(D) None of these
Ans – (B) 55.5 M
11. The molality of pure water is:
(A) 20
(B) 18
(C) 10
(D) 55.5
Ans – (D) 55.5
12. In the following strongest acid is: Most Important
(A) HCIO
(B) HClO3
(C) HCIO4
(D) HCIO2
Ans – (C) HCIO4
13. Isotonic solutions are the solutions having same : Most Important
(A) Concentration
(B) Osmotic pressure
(C) Surface tension
(D) Viscosity
Ans – (B) Osmotic pressure
14. Molal elevation constant is also called as:
(A) Cryoscopic constant
(B) Gas constant
(C) Ebullioscopic constant
(D) Freezing point depression constant
Ans – (C) Ebullioscopic constant
15. Which of the following has highest value of Van’t Hoff factor?
(A) 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3
(B) 0.1 M C6H12O6
(C) 0.1 M K2SO4
(D) 0.1 M NaCl
Ans – (A) 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3
16. Symbol for Cryoscopic constant is:
(A) P0
(B) Kb
(C) Kf
(D) None of these
Ans – (C) Kf
17. What is the value of Van’t Hoff factor (i) for K4[Fe(CN)6] ?
(A) 6
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) Zero
Ans – (B) 5
18. Which is most Basic ?
(A) PH3
(B) SbH3
(C) NH3
(D) ASH3
Ans – (C) NH3
19. What is the value of Van’t Hoff factor (i) for dilute solution of Al2(SO4)3 ?
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) 6
Ans – (C) 5
20. In which Bond Angle is maximum ?
(A) H2Sc
(B) H2O
(C) H2S
(D) H2Te
Ans – (B) H2O
21. Which is independent of temperature?
(A) Molality
(B) Normality
(C) Molarity
(D) Volume %
Ans – (C) Molarity
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 – Electrochemistry MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Conductance of an electrolytic solution depends:
(A) Nature of electrolyte
(B) Power of AC source
(C) Distance between two electrodes
(D) None of the above
Ans – (A) Nature of electrolyte
2. The metal that cannot be obtained by electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its salt is:
(A) Ca
(B) Ag
(C) Cr
(D) Cu
Ans – (A) Ca
3. Rust is mixture of :
(A) Fe2O3
(B) Fe2O3 and Fe(OH)3
(C) FeO and Fe(OH)3
(D) Fe3O4 and Fe(OH)3
Ans – (B) Fe2O3 and Fe(OH)3
4. The quantity of charge required to obtain 1 mol of Al from Al2O3.
(A) 1 F
(B) 6 F
(C) 3 F
(D) 2 F
Ans – (C) 3 F
5. Which of following statement is correct?
(A) Electrolysis of dil NaOH gives H2 at cathode & O2 at anode.
(B) Electrolysis of H2SO4 gives H2 at cathode & O2 at anode.
(C) Electrolysis of aq KF solution gives F2 at cathode.
(D) None of the above.
Ans – (B) Electrolysis of H2SO4 gives H2 at cathode & O2 at anode.
6. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of:
(A) Lone pair of electron
(B) Free valence electron
(C) Cations
(D) Anions
Ans – (B) Free valence electron
7. For the given cell reaction: Mg | Mg2+ || Cu2+ | Cu Most Important
(A) Mg as Cathode
(B) Cu as Cathode.
(C) Cu is oxidizing agent
(D) None of the above
Ans – (B) Cu as Cathode.
8. For the given cell reaction: Cu | Cu2+ || Ag+ | Ag
(A) Cu as cathode
(B) Ag as cathode
(C) Ag as oxidising agent
(D) None of the above
Ans – (B) Ag as cathode
9. Number of Faradays (F) required to reduce 1 mole of MnO4– into Mn2+. Most Important
(A) 5F
(B) 2F
(C) 1F
(D) 7F
Ans – (A) 5F
10. The SI Units of molar conductivity are:
(A) Sm-1mol-1
(B) Sm3mol-1
(C) Sm-2mol
(D) Sm2mol-1
Ans – (D) Sm2mol-1
11. Standard Electrode potential for Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is: Most Important
(A) 0.5 V
(B) + 1.0 V
(C) 0.0 V
(D) + 2.0 V
Ans – (C) 0.0 V
12. Fused NaCl on electrolysis gives on Cathode is:
(A) Chlorine
(B) Sodium
(C) Sodium Amalgam
(D) Hydrogen
Ans – (B) Sodium
13. In dry cell which of the following is the Electrolyte ?
(A) Potassium hydroxide
(B) Sulphuric acid
(C) Ammonium chloride
(D) Manganese dioxide
Ans – (D) Manganese dioxide
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 – Chemical Kinetics MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Role of a catalyst is to change:
(A) Gibbs energy of reaction
(B) Enthalpy of reaction
(C) Activation energy of reaction
(D) None of the above
Ans – (C) Activation energy of reaction
2. Unit of rate constant for a Zero order reaction is:
(A) mol L–1 s–1
(B) L mol–1 s–1
(C) L2 mol–2 s–1
(D) s–1
Ans – (A) mol L–1 s–1
3. Time required for 100% completion of a Zero order reaction is:
(A) t100% = a/k
(B) t100% = a.k
(C) t100% = a/2k
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) t100% = a/k
4. Arrhenius equation is represented by:
(A) K = AeEa/RT
(B) K = Ae–Ea/RT
(C) t1/2 = 0.693/K
(D) None of the above
Ans – (B) K = Ae–Ea/RT
5. During decomposition of an activated complex:
(A) Energy is always released
(B) Energy is always absorbed
(C) Energy does not change
(D) None of the above
Ans – (B) Energy is always absorbed
6. Identify the order of reaction from given rate constant K = 2.6×10–4 mol L–1S–1.
(A) First
(B) Zero
(C) Second
(D) None of these
Ans – (B) Zero
7. A catalyst increases the rate of reaction, then what will be the effect on rate constant ?
(A) Increases
(B) Decreases
(C) Not Changed
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) Increases
8. If rate constant for a Reaction is mole litre–1 second–1 then order of reaction is:
(A) Zero order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) Zero order
9. Identify the order of Reaction from the given rate constant K = 2.6×10–4 L Mol–1S–1 Most Important
(A) First
(B) Zero
(C) Second
(D) None of these
Ans – (C) Second
10. For a Reaction N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 the rate of reaction with respect to NH3 will be?
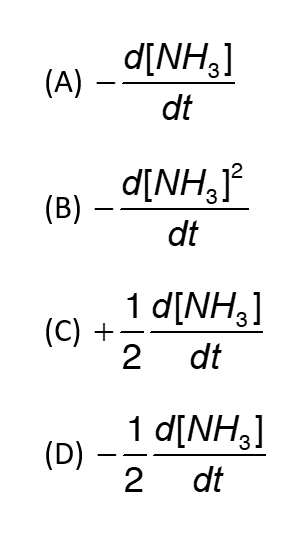
Ans – (C)
11. If Half life period of a first order reaction is 100 Seconds. There rate constant will be:
(A) 6.93 x 10-3 Second
(B) 6.93 x 10-2 Second
(C) .693 Second
(D) 6.93 Second
Ans – (A) 6.93 x 10-3 Second
12. Half-life period of a first order reaction depends upon :
(A) Concentration of reactants
(B) Concentration of products
(C) Rate constant of reaction
(D) None of these
Ans – (C) Rate constant of reaction
13. The units of rate constant for first order reaction is: Most Important
(A) Time-1
(B) Concentration-1 Time-1
(C) Concentration2 Time-2
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) Time-1
14. An example of Zero Order Reaction is:
(A) Thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface
(B) Hydrogenation of ethene
(C) Decomposition of N2O5
(D) Inversion of Sucrose
Ans – (A) Thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface
15. If rate of a reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants, then reaction is:
(A) Zero order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) Zero order
16. Rate constant for a reaction is Rate = K[A]2 [B]-3/2 the order of reaction is:
(A) 3.0
(B) 0.5
(C) 1
(D) -0.5
Ans – (B) 0.5
17. Identify the order of reaction from the given rate constant: K = 1.6 x 10-6 L mol-1S-1 Most Important
(A) Zero
(B) First
(C) Second
(D) None of these
Ans – (C) Second
18. A reaction is second order with respect to reactant. How is rate of reaction affected if concentration of reactant is reduced to half?
(A) 4 times
(B) 2 times
(C) 1/4 times
(D) 8 times
Ans – (C) 1/4 times
19. A reaction is second order with respect to reactant. How is rate of reaction affected ? If concentration of reactant is doubled ?
(A) 2 times
(B) 4 times
(C) 8 times
(D) 1/4 times
Ans – (B) 4 times
20. A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the rate law equation:
(A) Rate = K [A]2 [B]1
(B) Rate = K [A]1 [B]1
(C) Rate = K [A]1 [B]2
(D) Rate = K [A]2 [B]2
Ans – (C) Rate = K [A]1 [B]2
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 – The d and F block Elements MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. In the following strongest reducing agent is: Most Important
(A) PH3
(B) BiH3
(C) SbH3
(D) AsH3
Ans – (B) BiH3
2. Which of the following ion is colourless in aqueous solution?
(A) Fe2+
(B) Mn2+
(C) Ti3+
(D) Sc3+
Ans – (D) Sc3+
3. Which one is coloured ?
(A) Cu2Cl2
(B) [Sc(H2O)6]3+
(C) [Zn(H2O)6]2+
(D) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
Ans – (D) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
4. Which element does not show variable oxidation state ?
(A) Sc
(B) V
(C) Fe
(D) Hg
Ans – (A) Sc
5. Which of the following oxidation state is most common among the lanthanoids ?
(A) +4
(B) +3
(C) +2
(D) +5
Ans – (B) +3
6. The oxidation number of Cobalt in K[Co(CO)4] is
(A) +1
(B) -1
(C) +3
(D) -3
Ans – (B) -1
7. Which one is coloured?
(A) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
(B) Cu2I2
(C) [Sc(H2O)6]3+
(D) [Zn (NH3)6]2+
Ans – (A) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
8. Haber’s process is used to prepare:
(A) H2SO4
(B) NH3
(C) HCI
(D) O3
Ans – (B) NH3
9. What is the magnetic moment of Sc3+ ion ?
(A) 1.73 BM
(B) 0 BM
(C) 5.92 BM
(D) 2.83 BM
Ans – (B) 0 BM
10. Number of Unpaired Electrons in Ni2+ are:
(A) 0
(B) 2
(C) 8
(D) 4
Ans – (B) 2
11. Oxidation number of Pt in K2[PtCl6] is:
(A) +6
(B) +2
(C) +4
(D) Zero
Ans – (C) +4
12. What is the magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2- complex?
(A) 2.82 BM
(B) 1.82 BM
(C) 5.92 BM
(D) 1.41 BM
Ans – (A) 2.82 BM
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 – Coordination Compounds MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Which complex exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) [MnBr4]2+
(B) [Pt(NH3)3 CI]+
(C) [PtCl2(P(C2H5)3)2]
(D) [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+
Ans – (C) [PtCl2(P(C2H5)3)2]
2. What is the Co-ordination number in the [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 Compound?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 2
Ans – (C) 6
3. The Oxidation number of chromium in [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 is :
(A) +4
(B) +3
(C) –3
(D) +2
Ans – (B) +3
4. In the following chelating ligand is :
(A) OH–
(B) H2NCH2CH2NH2
(C) Cl–
(D) CN–
Ans – (B) H2NCH2CH2NH2
5. What is the co-ordination number in the (Co(NH3)5 (CO3)]Cl compound? Most Important
(A) 6
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 2
Ans – (B) 3
6. What is the coordination number in the K3 [Cr (C2O4)3] coordinate compound:
(A) 3
(B) 6
(C) 4
(D) 2
Ans – (B) 6
7. What is the co-ordination number of Cr in [Cr(en)3]3+ complex ?
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 6
(D) 4
Ans – (C) 6
8. What is the co-ordination number of cobalt in the [CoCl2(en)2]Cl compound?
(A) 6
(B) 4
(C) 8
(D) 2
Ans – (A) 6
9. What is the co-ordination number of aluminium in K3[Al(C2O4)3] compound ?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 2
(D) 6
Ans – (D) 6
10. What is the co-ordination number of platinum in [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] compound?
(A) 4
(B) 8
(C) 6
(D) 2
Ans – (A) 4
11. Which type of Isomerism present in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2 and [Co(NH3)4ClNO2]Cl
(A) Ionic
(B) Linkage
(C) Optical
(D) Geometrical
Ans – (A) Ionic
12. In the following in which metal of complex ion has zero oxidation number?
(A) [Cr(H2O)6]3+
(B) [CuCl4]2-
(C) [Fe(CO)5]
(D) [Fe(CN)6]3-
Ans – (C) [Fe(CO)5]
13. What is hybridization of Ni in [NiCl4]2- ?
(A) sp3d
(B) dsp2
(C) sp3d2
(D) sp3
Ans – (D) sp3
14. What is relation between [Co(NH3)5CI]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]CI ?
(A) Linkage isomers
(B) Coordination isomers
(C) Ionisation isomers
(D) Solvate isomers
Ans – (C) Ionisation isomers
15. Which type of Isomerism present in [Cr(NH3)Cl]Br and [Cr(NH3)5Br]Cl ?
(A) Linkage
(B) Geometrical
(C) Optical
(D) Ionic
Ans – (B) Geometrical
16. In the following complexes which metal has zero oxidation number ?
(A) [Fe(CN)6]3-
(B) [CuCl4]2-
(C) [Ni(CO)4]
(D) K4[Fe(CN)6]
Ans – (C) [Ni(CO)4]
17. In the following which is strongest Ligand?
(A) OH–
(B) NCS–
(C) CN–
(D) CO
Ans – (C) CN–
18. Which Element will show highest oxidation number ?
(A) Cr
(B) Mn
(C) Fe
(D) Zn
Ans – (B) Mn
19. Which is Ambidentate Ligand ? Most Important
(A) CO32-
(B) CN
(C) NO3–
(D) Br
Ans – (A) CO32-
20. The oxidation number of Cr in [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl is:
(A) +6
(B) +1
(C) +3
(D) Zero
Ans – (C) +3
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH is:
(A) 3° < 2° <1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° < 2° > 1°
(D) None of these
Ans – (B) 3° > 2° > 1°
2. A 1° alkyl halide would prefer to undergo :
(A) SN2
(B) SN1
(C) Elimination
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) SN2
3. Copper sulphate dissolves in excess of KCN to give :
(A) [Cu(CN)4]3–
(B) [Cu(CN)4]2–
(C) CuCN
(D) [Cu(CN)2]
Ans – (D) [Cu(CN)2]
4. Organic compound which shows complete stereochemical inversion during SN2 reaction : Most Important
(A) CH3Cl
(B) (CH3)2CH–Cl
(C) (CH3)3C–Cl
(D) None of the above
Ans – (A) CH3Cl
5. Which Metal has highest density?
(A) Pt
(C) W
(B) Os
(D) Hg
Ans – (B) Os
6. SN2 reaction will be fastest in :
(A) CH3Br
(B) CH3Cl
(C) CH3CH2Cl
(D) (CH3)2CHCl
Ans – (A) CH3Br
7. C6H5Cl + CH3CI + 2NO
 This reaction is:
This reaction is:
(A) Staphen
(B) Sendmeyer’s
(C) Fittig
(D) Wurtz-Fitting
Ans – (D) Wurtz-Fitting
8. Which of the following organic compounds are formed by Wurtz reaction?
(A) Alcohols
(B) Hydrocarbons
(C) Haloalkanes
(D) Haloarenes
Ans – (B) Hydrocarbons
9. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo : Most Important
(A) SN2
(B) SN1
(C) Elimination
(D) None of these
Ans – (A) SN2
10. CH3Cl A
P, P is :
(A) CH3CH2Cl
(B) CH3CH2NH2
(C) C2H5CN
(D) C3H8
Ans – (B) CH3CH2NH2
11. Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment ? Most Important
(A) CHCl3
(B) CH3Cl
(C) CH2Cl2
(D) CCl4
Ans – (C) CH2Cl2
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 – Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Acid anhydrides on reaction with 1° amine gives:
(A) Amide
(B) Imide
(D) None of these
(C) Imine
Ans – (A) Amide
2. Alkyl halides are prepared from alcohol by treating with:
(A) HCI + ZnCl2
(B) H2SO4 + KI
(C) NaCl + H2SO4
(D) None of the above
Ans – (A) HCI + ZnCl2
3. Molecular formula of Ethers is: Most Important
(A) CnH2n+1O
(B) CnH2nO
(C) CnH2n+2O
(D) None of the above
Ans – (C) CnH2n+2O
4. Which of the following is most acidic ? Most Important
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Cyclohexanol
(C) Phenol
(D) m-chlorophenol
Ans – (D) m-chlorophenol
5. Williamson Synthesis is used to prepare: Most Important
(A) Alcohol
(B) Amine
(C) Ketone
(D) Ether
Ans – (D) Ether
6. In the reaction 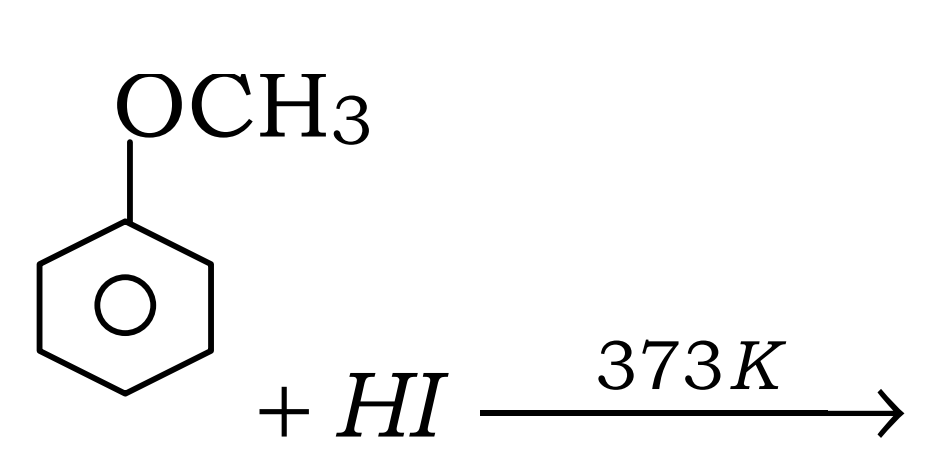 A + B A and B are :
A + B A and B are :
(A) C6H5I, CH3OH
(B) C6H5OH, CH3I
(C) C6H5CH2OH, CH3I
(D) CH3CH2I, C6H5OH
Ans – (B) C6H5OH, CH3I
7. Which is weakest acid in the following?
(A) CH3OH
(B) (CH3)2CHOH
(C) CH3CH3OH
(D) (CH3)3COH
Ans – (D) (CH3)3COH
8. CH3CH2OH A’, A’ will be : Most Important
(A) CH2=CH2
(B) C2H5OCH3
(C) (C2H5)2O
(D) CH3CH2CH2CH3
Ans – (A) CH2=CH2
9. Anisole  with Hi at 373 K temperature will give :
with Hi at 373 K temperature will give :
(A) C6H5I + CH3OH
(B) C6H5OH + CH3I
(C) C6H5CH2OH + CH3I
(D) CH3CH2I + C6H5OH
Ans – (B) C6H5OH + CH3I
10. Arrange the following in order of increasing their Acidic strength:
(A) CH3OH
(B) C2H5OH
(C) Phenol
(D) p- Nitrophenol
Ans – (D) p- Nitrophenol
11. CH3-CH2-OH X what is X? Most Important
(A) CH2 = CH2
(B) C2H5 – O – C2H5
(C) CH3 – O – CH2 – CH3
(D) CH3CH2HSO
Ans – (A) CH2 = CH2
12. In the preparation of alkyl halide from alcohol which of the following reagent is preferred?
(A) HX + ZnCl2
(B) PX3
(C) PCl5
(D) SO2Cl2
Ans – (C) PCl5
13. Which is strongest acid in the following ? Most Important
(A) CH3OH
(B) CH3CH2OH
(C) (CH3)2CHOH
(D) (CH3)3COH
Ans – (A) CH3OH
14. Which one is the strongest acid ?
(A) Ethanol
(B) Phenol
(C) Methanol
(D) p-Nitrophenol
Ans – (D) p-Nitrophenol
15. C2H5OC2H5 + HI → A + B, A and B are:
(A) C2H5OH, C2H5I
(B) C2H5OH, CH3I
(C) C2H5CHO + CH3I
(D) C2H5I, CH3OH
Ans – (A) C2H5OH, C2H5I
16. Reaction of Benzene diazonium chloride with ethanol will give :
(A) Benzene
(B) Benzamide
(C) Benzenamine.
(D) Phenol
Ans – (A) Benzene
17. Which is Least Acidic ?
(A) C2H5OH
(B) CH3COOH
(C) C6H5OH
(D) CICH2COOH
Ans – (A) C2H5OH
18. In the reaction C6H5OCH3 + HI A+B, A and B are
(A) C6H5I, CH3OH
(B) C6H5OH, CH3I
(C) C6H5CH2OH, CH3I
(D) CH3CH2I, C6H5OH
Ans – (B) C6H5OH, CH3I
19. A tertiary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo :
(A) SN2
(B) Elimination
(C) Addition
(D) SN1
Ans – (B) Elimination
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 – Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Which on heating with aqueous KOH, produces acetaldehyde ?
(A) CH3 — CH — Cl2
(B) CH3 — CO — Cl
(C) CH3 — CH2 — Cl
(D) CH3 — Cl — CH2 — Cl
Ans – (A) CH3 — CH — Cl2
2. lodoform test is not given by: Most Important
(A) 2-Pentanone
(B) 3-Pentanone
(C) Ethanol
(D) Ethanal
Ans – (B) 3-Pentanone
3. IUPAC name of Acetic acid is: Most Important
(A) Methanal
(B) 2- Pentanone
(C) Ethanoic acid
(D) Methanoic acid
Ans – (C) Ethanoic acid
4. Which metal carbonyl has the strongest C-O bond?
(A) Mn(CO)6+
(B) Cr(CO)6
(C) V(CO)6
(D) Fe(CO)5
Ans – (A) Mn(CO)6+
5. A strong base can abstract an α-hydrogen from:
(A) Ketone
(C) Alkene
(B) Alkane
(D) Amine
Ans – (A) Ketone
6. In the following strongest acid is:
(A) CH3CH2COOH
(B) CH3COOH
(C) C6H5COOH
(D) C6H5CH2COOH
Ans – (C) C6H5COOH
7. What type of organic compound are prepared by Gatterman-Koch reaction?
(A) Aliphatic Aldehyde
(B) Aromatic Ketone
(C) Aliphatic Ketone
(D) Aromatic Aldehyde
Ans – (D) Aromatic Aldehyde
8.  , this reaction is:
, this reaction is:
(A) Etard reaction
(B) HVZ reaction
(C) Rosenmund reduction
(D) Gatterman reaction
Ans – (C) Rosenmund reduction
9. Aldehydes and Ketones can be distinguished by:
(A) Conc. H2SO4
(B) Anhyd. ZnCl2
(C) Tollens’ Reagent
(D) Conc. HCL
Ans – (C) Tollens’ Reagent
10. Which is the strongest acid ?
(A) CH3COOH
(B) CH3CH2COOH
(C) CICH2COOH
(D) FCH2COOH
Ans – (D) FCH2COOH
11. In the following reaction, product P is, 
P :

Ans – (B)
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 – Amines MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1.Hoffman Bromamide degradation reaction involve :
(A) Ar–NH2
(B) Ar–CONH2
(C) Ar–NO2
(D) None of these
Ans – (B) Ar–CONH2
2. Which of the following is a 3° amine?
(A) Methylamine
(B) Triethyl amine
(C) Ethylamine
(D) t-butylamine
Ans – (B) Triethyl amine
3. Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction form:
(A) Ar – CONΗ2
(B) Ar – NO2
(C) Ar – NH2
(D) Ar – OH
Ans – (C) Ar – NH2
4. What is the name of this reaction? ArN2+X– ArCl + N2 + CuX
(A) Coupling reaction.
(B) Balz-Schiemann Reaction
(C) Gattermann reaction
(D) Sendmeyer reaction
Ans – (C) Gattermann reaction
5. CH3CONH2 P, P is:
(A) CH3CN
(B) CH3NH2
(C) CH3Br
(D) CH3OH
Ans – (B) CH3NH2
6. C2H3NH + CHCl3 + KOH P, P is:
(A) C2H5Cl
(B) C2H5OH
(C) C2H5NC
(D) C2H5NHCH3
Ans – (A) C2H5Cl
7. Hofmann bromamide degradation reaction involve :
(A) C6H5NH2
(B) C6H5COΝΗ2
(C) C6H5NO2
(D) C6H5OH
Ans – (B) C6H5COΝΗ2
8. Which is a tertiary amine?
(A) t-butylamine
(B) Ethylamine
(C) N-Methylethylamine
(D) Triethylamine
Ans – (D) Triethylamine
9.  ; what is X?
; what is X?

Ans – (B)
10. Which of the following is most acidic ?

Ans – (A)
11.  , P is:
, P is:

Ans – (A)
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 – Biomolecules MCQ Important Question Answer 2025
1. Which of the following is stored in liver of animals ?
(A) Amylose
(B) Cellulose
(C) Amylopectin
(D) Glycogen
Ans – (D) Glycogen
2. Which base is present in DNA but not in RNA ? Most Important
(A) Thyamine
(B) Cytosine
(C) Uracil
(D) Guanine
Ans – (C) Uracil
3. In the following which is not a Monosaccharide sugar?
(A) Glucose
(B) Fructose
(C) Mannose
(D) Maltose
Ans – (D) Maltose
4. Which Vitamin is soluble in water?
(A) Vitamin D
(B) Vitamin K
(C) Vitamin E
(D) Vitamin B
Ans – (D) Vitamin B
5. Riboflavin is:
(A) Vitamin B
(B) Vitamin A
(C) Vitamin C
(D) Vitamin D
Ans – (A) Vitamin B
6. Vitamin B1 is known as:
(A) Ascorbic acid
(B) Thiamine
(C) Riboflavin
(D) Pyridoxine
Ans – (B) Thiamine
7. The Vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood is :
(A) Vitamin B1
(B) Vitamin D
(C) Vitamin K
(D) Vitamin C
Ans – (C) Vitamin K
8. Glycogen is an example of:
(A) Polysaccharide
(B) Disaccharide
(C) Monosaccharide
(D) Protein
Ans – (A) Polysaccharide
9. Which of the following amino acids is not optically active ? Most Important
(A) Alanine
(B) Glycine
(C) Valine
(D) Leucine
Ans – (B) Glycine
10. The Vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood is :
(A) Vitamin C
(B) Vitamin D
(C) Vitamin B1
(D) Vitamin K
Ans – (D) Vitamin K
11. Disaccharide is:
(A) Starch
(B) Fructose
(C) Lactose
(D) Cellulose
Ans – (C) Lactose
12. Enzymes are:
(A) Nucleic acids
(B) Fats
(C) Carbohydrates
(D) Proteins
Ans – (D) Proteins
13. Glycogen is an example of:
(A) Protein
(B) Polysaccharide
(C) Monosaccharide
(D) Disaccharide
Ans – (B) Polysaccharide