Class 6 Geography India : Climate, Vegetation and Wildlife chapter 8 notes NCERT Solution in Hindi. NCERT Class 6 Geography Notes, Textual Question Answer and Important Question Answer also Available for Various Board Students like HBSE, CBSE, UP board, Mp Board, RBSE and some other State Boards.
Also Read:- Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution
NCERT Solution for Class 6 Geography Chapter 8 India : Climate, Vegetation and Wildlife Notes for students.
India : Climate, Vegetation and Wildlife Class 6 Geography Chapter 8 Notes
-> Weather :- It is about day to day changes in the atmosphere. It includes changes in temperature, rainfall and sunshine.
Major Seasons in India :-
(i) Cold Weather Season or Winter – During this season cool, dry wind blow from north to south usually in the month from December to February.
(ii) Hot Weather Season or Summer – During this season hot and dry winds called loo, blow during the day.
(iii) South West Monsoon or Rainy Season – In this season winds blow from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal towards the land. When these winds carrying moisture strike the mountains, rainfall occurs.
(iv) Season of Retreating Monsoons or Autumn Season – During this season winds move back from the mainland to the Bay of Bengal . The southern parts of India receives rainfall in this season.
Climate – It is about the average weather conditions, which have been measured over many years. The climate of a place is affected by its location, altitude, distance from the sea, and relief. The climate of India has been described as Monsoon type. Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives the world’s highest rainfall in the world.
Natural Vegetation – The grasses, shrubs and trees, which grow on their own without interference or help from human beings are called natural vegetation. Due to varied climatic conditions, Vegetation of India can be divided into five types as
(i) Tropical Rain Forest – These forests occur in the areas which receives heavy rainfall. Many species of trees are found in these forests which shed their leaves at different times of the year. As a result they always appear green and are called evergreen forest.
Trees found – Mahogany, ebony and roeswood.
Areas – Andaman and Nicobar islands, parts of North-Eastern States and Western Ghats.
(ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests – These forests are also called monsoon forests. They are less dense, shed their leaves at a particular time of the year.
Trees found- sal, teak, peepal, neem and shisham.
Areas – Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Maharashtra.
(iii) Thorny Buses – It is found in the dry areas of the country . The leaves are in the form of spines to reduce the loss of water.
Trees/Species – Cactus, Khair, Babool, Keekar.
Areas – Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Eastern slopes of Western Ghats and Gujarat.
(iv) Mountain Vegetation – A wide range of species is found in mountains according to variation in height. At a height between 1500 to 2500m most of the trees are conical in shape. These trees are called coniferous trees.
Trees/Species – Chir, Pine and Deodar.
Areas – In mountain areas like Himachal, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh etc.
(v) Mangrove Forests – These forests can survive in saline water.
Trees – Sundari is a well known species of trees in mangrove forest.
Areas – Sunderbans in West Bengal and Andaman and Nicobar islands.
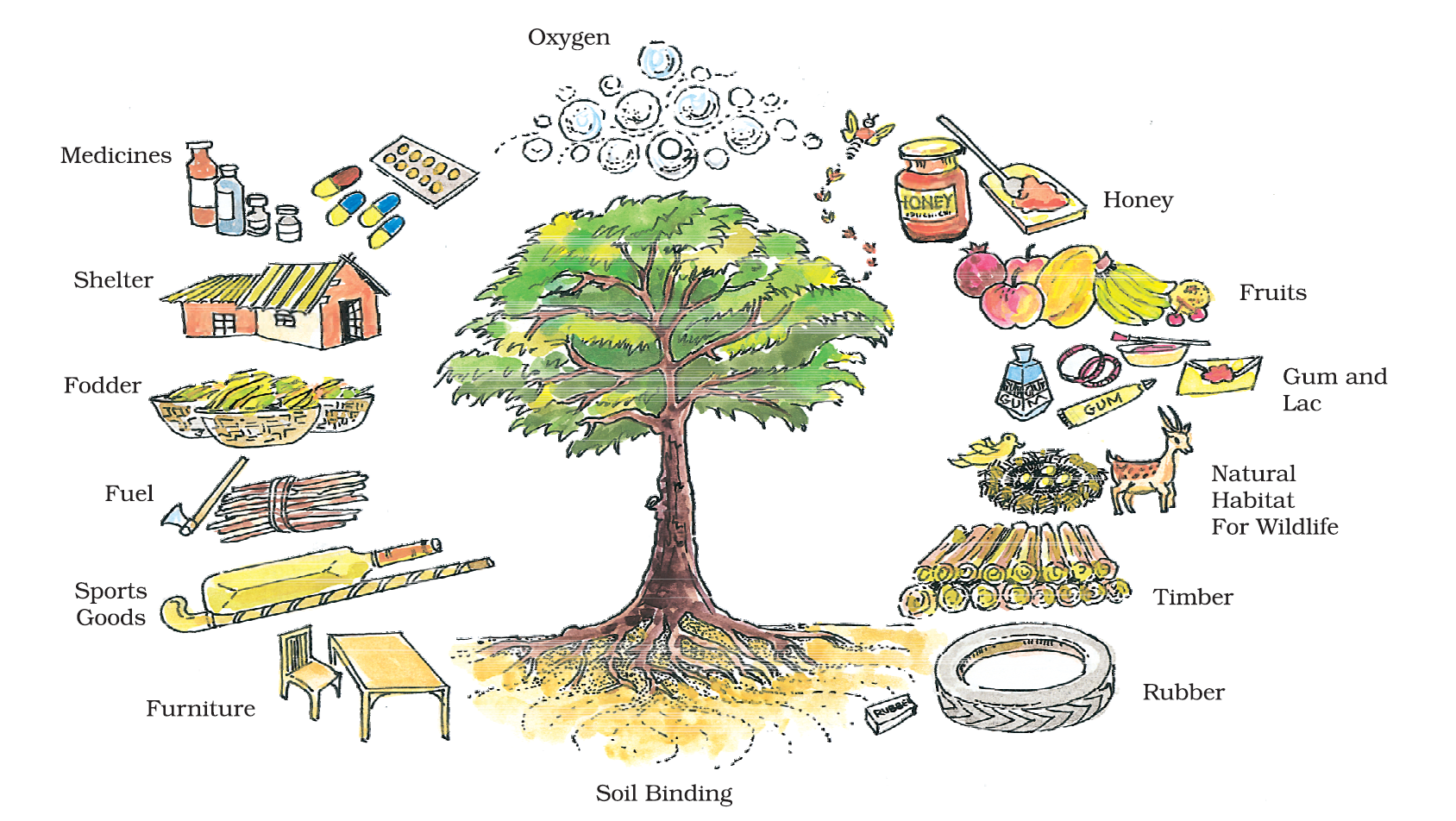
Why Are Forests Necessary?
(i) They provides us oxygen which is essential for lives.
(ii) Roots of plants bind the soil by which they control soil erosion.
(iii) Forests provide us with timber for furniture, fuel , wood, fodder, medicinal plants and herbs, lac, honey, gum etc.
(iv) Forests are the natural habitat of wild life.
Wildlife –
(i) The tiger is our national animal mainly found in Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Karnataka.
(ii) Gir forest in Gujarat is the home of Asiatic lions. Elephants and one-horned rhinoceroses found in forests of Assam. Wild goats, snow leopards, bears etc. are found in the Himalayan region.
(iii) The peacock is our national bird. Other common birds are parrots, pigeons, ducks and bulbul. Bird Sanctuaries are created to give birds their natural habitat.
(iv) The Government has started Project Tiger(1973) and Project Elephant(1992) to protect animals.
(iv) Wildlife week in the first week of October is celebrated every year.
(v) Cobras and Kraits are the common species found in India.