NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise short Notes Solution For School Students of Class 9th. We also Provides Notes and Important Questions for Class 9 Science. NCERT Class 9th Science book is applied in mostly boards like CBSE, HBSE, RBSE, Up Board, MP Board and also some other state boards.
Also Read:- Class 9 Science NCERT Solution
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Short Notes for CBSE, HBSE and Other Boards Solution.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science Notes
Matter :- Anything which occupy space and having mass is called matter. It is made up of tiny particles. Particles of matter have space between them and they attract each other.
States of Matter : There are five states of matter i.e. Solid, Liquid, Gas, Plasma and Bose-Einstein Condensate.
We will discuss only three states in this chapter.
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| Have definite shape and definite volume | Having indefinite shape and definite volume | Neither definite shape nor definite volume |
| Having strong intermolecular force of attraction | Weak intermolecular force | very weak intermolecular force of attraction |
| Very less intermolecular space | Large intermolecular space | Very large intermolecular space. |
| Solids cannot be compressed. | Liquids can be compressed. | Gases can be highly compressed. |
| Have high density | Have low density | Very low density |
Change in State of Matter :
Pressure and Temperature determines the state of a substance, whether it will be solid, liquid or gas.
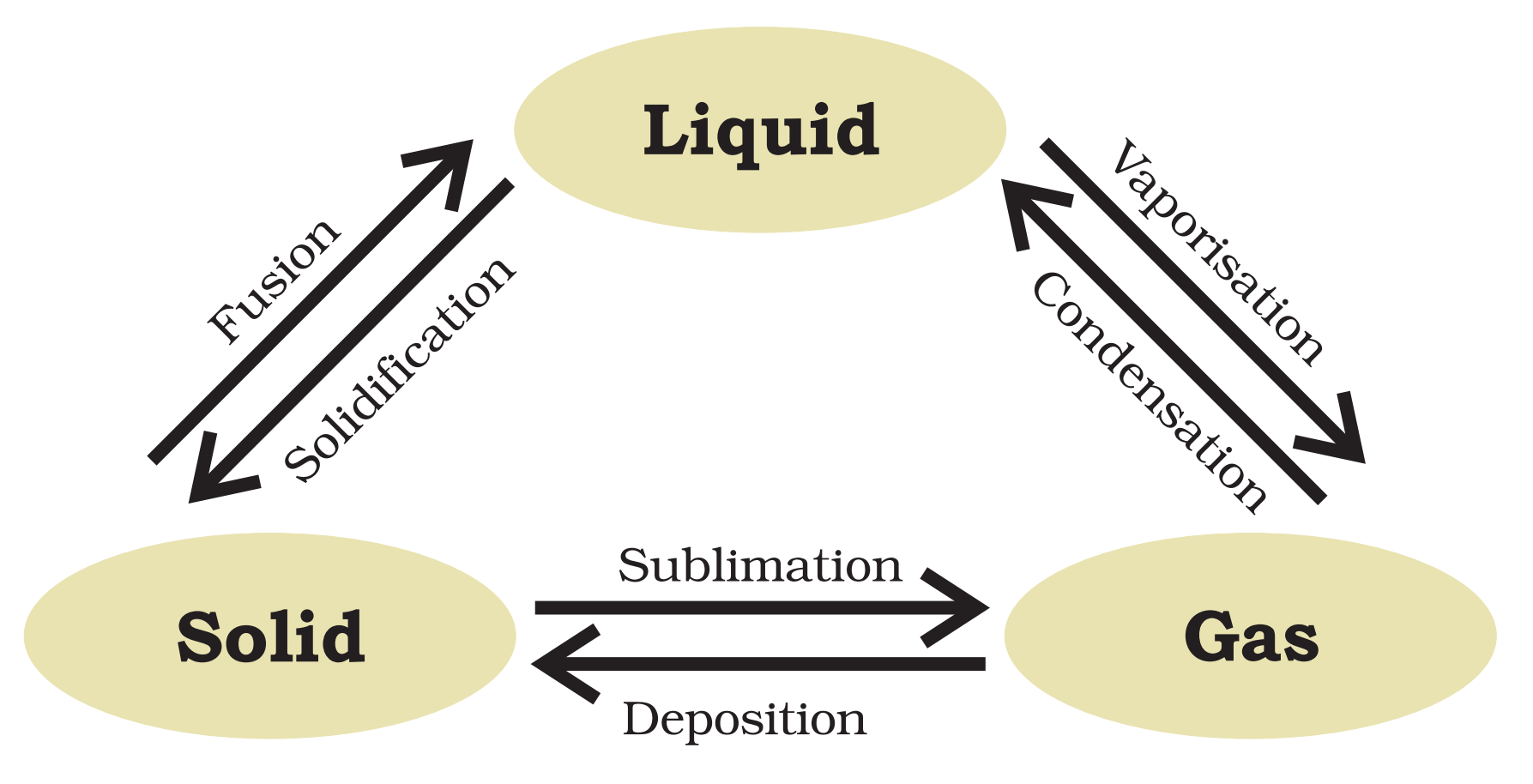
1. Solid to Liquid
Melting Point : The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point. Melting point of ice is 273.15 K.
Fusion : The process of melting, that is, change of solid into liquid state is also known as fusion. During melting , temperature of solid remains same.
Latent Heat of fusion : The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion. Particles in water at 0° C have more energy as compared to particles in ice at the same temperature.
2. Liquid to Gas
Boiling point : The temperature at which a liquid start boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
Evaporation : The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Factors affecting evaporation :
(i) If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases.
(ii) With the increase of temperature, evaporation increases.
(iii) If the humidity in air is high, the rate of evaporation is low.
Process of Evaporation :
- We wear cotton clothes in summer. ( During summer, we perspire more. and cotton being a good absorber of water helps in absorbing the sweat and exposing it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation.)
- Our palm feel cold when we put some acetone (nail polish remover) on it. (The particles gain energy from our palm or surroundings and evaporate using the palm to feel cool. )
- The water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer. (This is due to liquid keeps on evaporating . The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to regain the energy lost during evaporating. This absorption of energy from the surroundings make the surroundings cold.)
- A desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day. ( because on a hot dry day temperature is high and humidity is less which helps in better evaporation. Due to higher rate of evaporation is gives better cooling effect. )
- We see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water. (the water vapour present in air, on coming in contact with the cold glass of water, loses energy and gets converted to liquid state, which we see as water droplets. )
3. Solid to Gas or gas to solid
Sublimation : A Change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called sublimation. eg – camphor.
Deposition : The direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called deposition. eg – water vapours to ice.
| Quantity | Unit |
| Temperature length Mass Weight Pressure |
Kelvin (K) metre (m) Kilogram (kg) Netwon (N) Pascal (Pa) |
Other important :
- CNG = Compressed Natural Gas
- LPG = Liquefied Petroleum Gas
- Dry Ice = Solid Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Acetone = Nail Polish remover
- K = 273 + °C